Market-Manage
What is market
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
solve the problem in a marketing way.
apple nike 'haagen dazs'
demand & supply
what is marketed ?
- Goods
- service
- Events
- Experiences 体验
- Information
- idea
- Place
- People
- Properties
- Organizations
news form market
Bloomberg Businessweek - Bloomberg
characters of service
• Intangibility: Services cannot be seen, tasted, felt, heard, or smelled before purchase. • Inseparability: Services cannot be separated from their providers. • Variability: Quality of services depends on who provides them and when, where and how. • Perishability: Services cannot be stored for later sale or use.
+ evolution of market
- 1920 production 生产
- 1930 product 产品
- 1960 selling 销售
- 2000 marketing 营销 (oversupply )
- 2010 societal marketing 社会营销 【公司,消费者,社会】
production concept
End of 19th century to 1920’s (1850s) • Assumption: Consumers will favor products that are available and highly affordable • Management should therefore focus on cutting costs, and improving production and distribution efficiency
product
• ~1930’s • Assumption: Consumers will favor high quality products • Management should focus on quality, developing innovative new products
selling concept
• ~1960’s • Assumption: Consumers will not buy enough of the organization’s products unless the organization undertakes a large – scale selling and promotion effort. • “Sell what we have. Creative advertising and selling will overcome consumers’ resistance and convince them to buy.” • Management should focus on aggressive selling efforts
Marketing Concept
• 2000’s~ • oversupply • Assumption: “The consumer is king! Find a need and fill it (better than competitors can).” • Management should focus on providing greater value than competitors
市场深层需求导向,
Societal Marketing Concept
• 2010’s • An organization should determine the needs, wants, and interests of target markets and deliver the desired satisfactions more effectively and efficiently than competitors in a way that maintains or improves the consumer’s and society’s well – being
company --- consumers --- society
TOMS, shoes one for one Nike, just do it
Example of Unilever: Sustainable Living Plan
conclude
What is the major driving force of the evolution of concepts?
competition
market environment analysis
A typical process of making marketing decisions
- environmental analysis
- External [PESTEL(政治、经济、社会文化宗教-religion、技术、法律), Porter's five forces()]
- Internal [SWOT]
- STP
- Segmentation
- Targeting
- Positioning
- Marketing mix formulation
- 4P
PESTEL Analysis
- competition
- technology
- economy
- culture
- political-legal
- geography and infrastructure
- structure of distribution
- (Natural) Environmental factors
Income Group by per Capita GNI % of World
| Class | GDP % of World | Population |
|---|---|---|
| High-income countries | GNI per capita ≥ $12,696 64 | 16% |
| Upper-middle-income countries | ||
| Lower-middle-income countries | ||
| Low-income countries |
GNI per capita ≥ $4,096 but ≤ $12,695 28 35%
GNI per capita ≥ $1,046 but ≤ $4,095 8 40%
GNI per capita < $1,045 0.75 9%
cultural
Hofstede’s Cultural Dimension Theory
Porter five Competitive analysis
- Competitive rivalry (竞争对手)
- Threat of substitutes
- Bargaining power of customers (客户议价能力)
- Bargaining power of suppliers (供应商的议价能力)
- Threat of new entrants
竞争对手分析
数量,差异度,行业发展,广告,
new entrants
差异性,规模化,切换成本,品牌忠诚度,政策,分发渠道。
SWOT-Internal Analysis
优劣,危机
+ STP
-
Segmentation
Identify and profile distinct groups of buyers with similar needs.
-
Targeting
Select one or more market segments to enter considering segment size and growth, segment attractiveness, and fit with company strategy.
-
Positioning
For each target segment, establish and communicate the key distinctive benefit(s) of the company’s market offering.
the BCD process of positioning
benefit , Concept (unique ) , Delivery (4P)
常见误区:传递太多功能,让人怀疑。
+ 品牌
品牌价值
recognition , referals , 稳定期望,connect ,


Resonance 共鸣

Brand Laddering
- Feature
- Benefits 直接
- Rewards 间接
- Emotional
Brand dilution 品牌稀释

+ 4P

Product Component Model

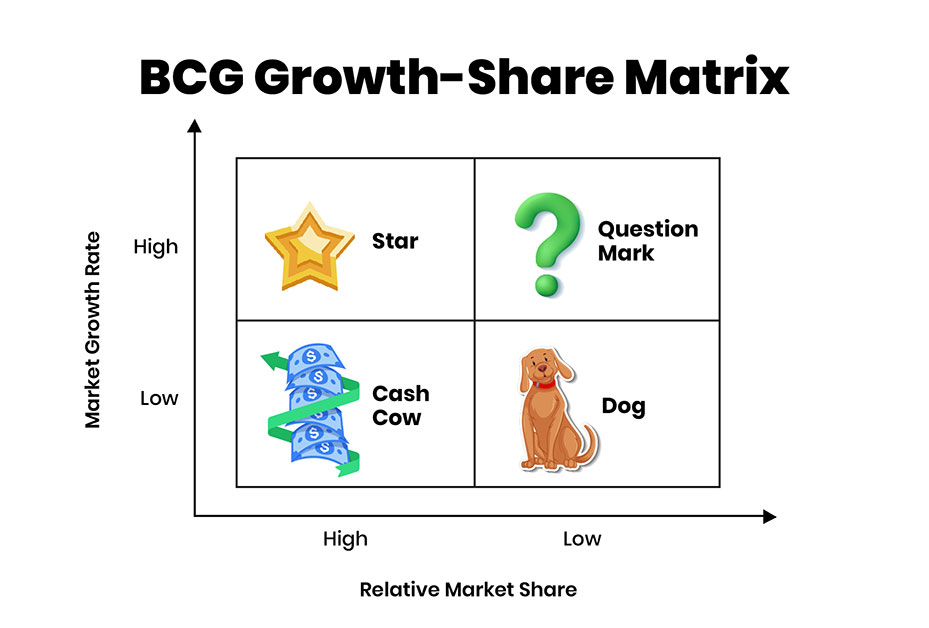
BCG Growth-Share Matrix
Price
产品定价的4种方法
- 成本
- 竞争对手
- 客户价值
- skimming vs Penetration Strategies (撇脂策略,渗透策略)
📈 撇脂策略和渗透策略在市场营销中各有什么优缺点?
撇脂策略(Skimming Strategy)和渗透策略(Penetration Strategy)是市场营销中的两种不同定价策略,它们各自有不同的优缺点。
成本策略
优:简单,公平,财务稳健。
缺:利润不最大,客户不关心你的成本,也不知道。
竞争策略
同质,价格敏感,行业老二、老三。
缺点:关注别人,创新不足,价格战争 。
价值定价
Price as a Function of Temperature 。
比如高峰期的加价打车 。
撇脂策略:market skimming
- 优点:
- 可以在产品生命周期的早期阶段迅速收回投资并实现利润最大化。
- 通过高价策略,可以创建产品的高端品牌形象。
- 在市场竞争不激烈时,可以利用价格优势来限制需求的过快增长,同时为后续的降价留出空间。
- 缺点:
- 高价可能会限制市场需求,导致销量较低。
- 容易吸引竞争对手进入市场,尤其是在产品差异化不明显的情况下。
- 如果市场对价格敏感,高价可能会导致消费者寻求替代品或竞争对手的产品。
渗透策略: market penetration
- 优点:
- 通过低价可以迅速占领市场,增加销量。
- 微利策略可以阻止竞争对手进入市场,增强企业的市场竞争力。
- 随着销量的增加,成本可能会降低,从而实现规模经济。
- 缺点:
- 利润率较低,可能需要更大的销量来实现盈利。
- 低价可能会影响产品的品牌形象,使得未来提价变得困难。
- 如果市场需求对价格不够敏感,低价策略可能不会带来预期的销量增长。
在选择这两种策略时,企业需要考虑产品的特性、目标市场、竞争环境以及自身的财务状况和长期战略目标。撇脂策略适合于那些具有独特卖点、目标市场对价格不敏感、且希望建立高端品牌形象的产品。而渗透策略则适合于那些市场对价格敏感、希望快速扩大市场份额、且能够通过规模经济降低成本的产品。
产品组合定价
价格线,分层定价
附属品定价
案例: 漫威
消费者对于价格的记忆最低。为什么可口可乐这么多年不涨价。
Place & Channel
商流和物流高度分离,商业高度发达。



中间商的作用
物理分发,销售活动,库存,服务,信息,市场,谈判。。。
push vs Pull Strategy

在渠道管理中,"push"(推式)和"pull"(拉式)策略是两种不同的市场推广方法,它们在如何将产品推向市场和消费者方面有着本质的区别。
Push Strategy(推式策略):
- 定义:推式策略是一种制造商主动将产品推向市场的方法。制造商通过销售团队、促销活动和渠道激励来推动产品通过分销渠道,直到产品到达最终消费者手中。
- 特点:制造商在推式策略中扮演积极的角色,通过各种激励措施(如折扣、返点、促销活动等)来鼓励分销商、零售商积极销售产品。
- 适用情况:推式策略适用于产品需求稳定、市场竞争激烈、需要快速分销的情况。它可以帮助制造商快速占领市场份额,但可能需要较大的营销和销售投入。
Pull Strategy(拉式策略):
- 定义:拉式策略是通过吸引最终消费者对产品的兴趣和需求,从而拉动产品通过分销渠道。制造商通过广告、促销活动和品牌建设来吸引消费者,使消费者向零售商和分销商表达对产品的需求。
- 特点:拉式策略侧重于建立品牌知名度和消费者忠诚度,通过满足消费者的需求和偏好来驱动销售。制造商通常通过广告、公关活动和社交媒体营销来吸引消费者。
- 适用情况:拉式策略适用于产品具有独特卖点、目标市场对品牌有较高认知度、消费者对产品有明确需求的情况。它可以帮助建立长期的品牌忠诚度,但可能需要较长的时间来见效。
区别:
- 主动与被动:推式策略是制造商主动推动产品销售,而拉式策略是通过吸引消费者需求来被动拉动产品销售。
- 成本与控制:推式策略可能需要更多的销售和营销成本,但制造商对销售过程有较高的控制力。拉式策略可能需要较长时间来建立品牌和消费者需求,但一旦成功,可以减少对渠道的依赖。
- 市场反应:推式策略可以快速响应市场变化,通过渠道激励来调整销售策略。拉式策略则需要根据消费者反馈和市场趋势来调整品牌和产品策略。
在实际应用中,许多企业会结合使用推式和拉式策略,以实现最佳的市场覆盖和销售效果。
渠道策略的选择
总结的讲,从市场,产品,制造,销售策略,4个维度决策。

intensive : all available outlets to distribute product.
selective: using only some available outlets to distribute a product.
exclusive: using a single outlet in a fairly large geographic area to distribute product.
Promotion/Integrated Marketing communications
advertising appeal : rational , emotional
广告
案例: 招商银行,留学生,信用卡,番茄炒蛋。水中贵州-百岁山。
销售促销策略包括:
- 产品试用装,
- 优惠券,
- 赠品,
- 竞赛,
- 回扣,
- 货架费,
- 频率计划,顾客忠诚度计划,
- 降价,
- 购买即赠礼品,
- 店内演示,
- 销售点(POP)展示。
- 。。。
《无价》